Alans, Alani, Alanliao, Aorses, As, Asii, Asses, Balanjar, Barsils, Belenjers, Burtas, Gelons, Halans, Iass, Iazyg, Ishkuza, Ishtek, Jass, Jats, Lan, Ostyak, Ovs, Rhoxolani, Steppe Alans, Yass, Yancai and other variations
Subdivisions and ethnic affiliates
Alans, Burtas, Rhoxolani, Wusüns, Yasses, Yazygs
Etymology
Türkic alan “field, plain”, hence Ch. calque Yancai/ Yantsai 奄蔡 “vast steppe”, Alan 阿蘭
Generally synonymous with Türkic as, yas “Low-Lander”
Synonymous with Türkic sabana, saban “field, steppe”
Contrasted with Tochar, Tokhar, Togar, Dagar, Taur, Togarmah “mountaineer” from Türkic Tag/Dag/Tau/Tay “mountain” + ar “people, men”, and Saka “piedmonter, foot-hiller”, the people of the mountains.
650 BC-1400 AD
Yancai Alans
300 BC – 0 AD
Yazyg Alans
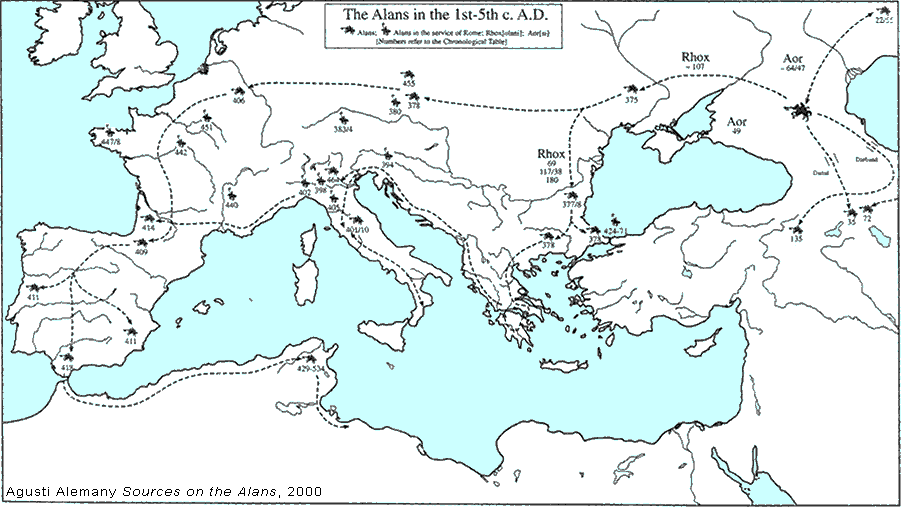
Alans
0-500 AD
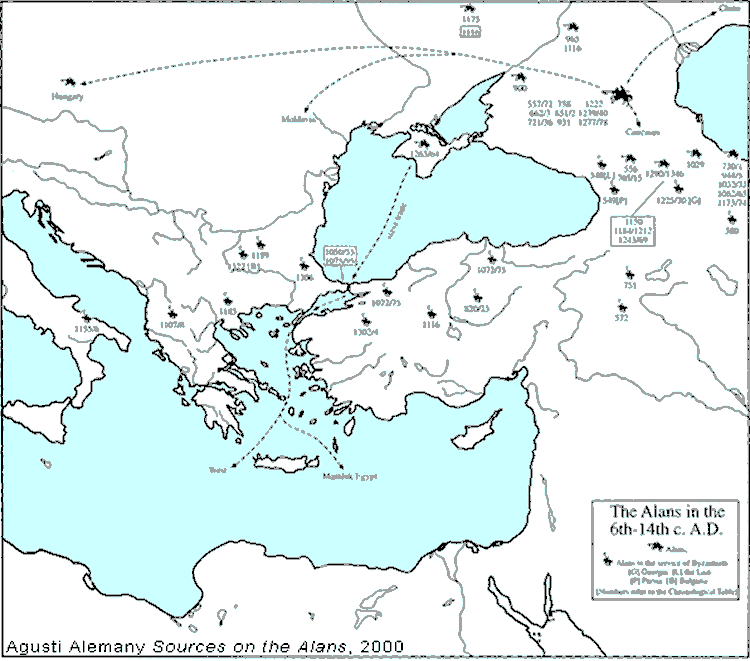
Alans
500 – 1400 AD
Amortica Alans
400-600 AD
Caucasus Alans
900-1000 AD
Caucasus Alans
1000-1400 AD
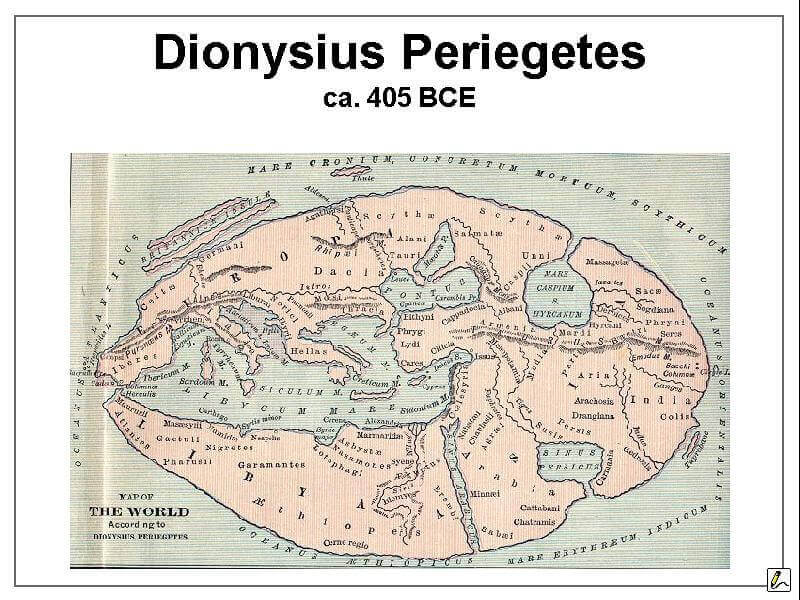
AD 124 Dionysius Periegetes Map 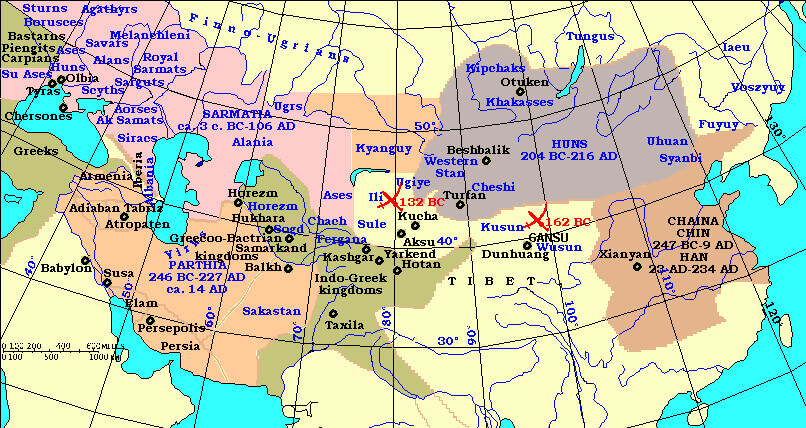
Hun Empire 20 4B.C. – 216 A.D. 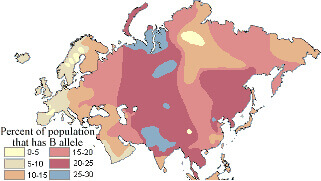
Map fo Blood-In-Eurasia 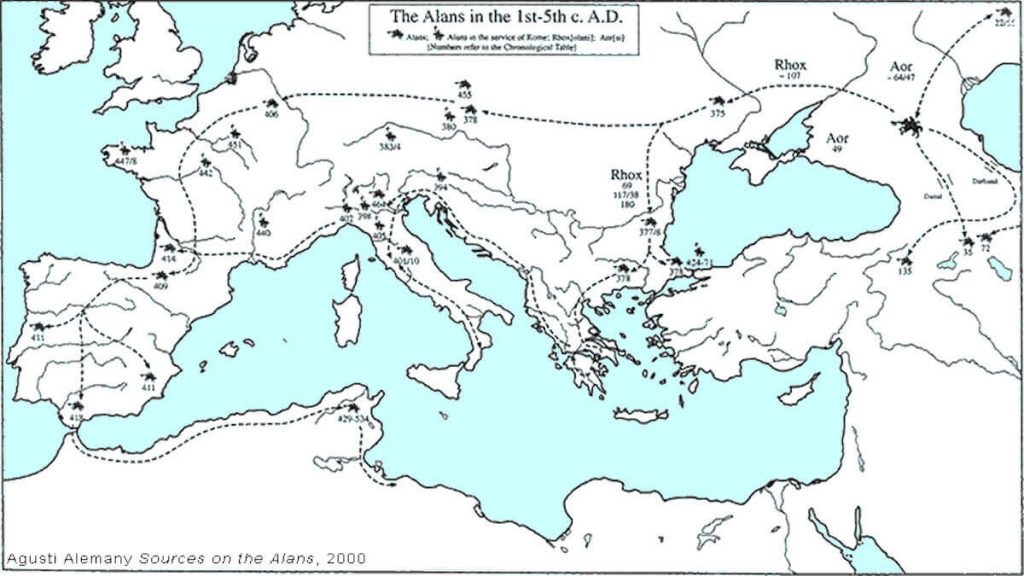
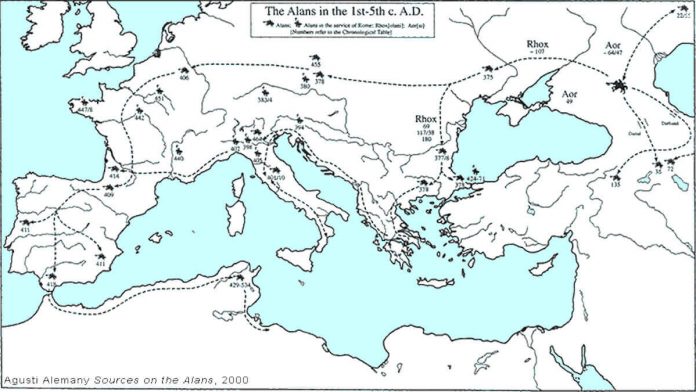
The Alans in the 1st-5th C. A.D. 
Death of Dengizih (Diggiz)
| DATELINE | ||
|---|---|---|
| Time | Events | |
| 650 BC | Ases are first mentioned in Assyrian sources as the Scythian name Ishkuza = Ish-Oguz or Ish-kiji, with the same semantic, where Ish is a variation of ethnonym As, and Oguz or kiji stand for people. | |
| 500 BC | Tribe of Aderbics, part of Masguts/Massagetae, sent 40 thousand infantrymen and 2 thousand horsemen to the camp of Darius the Great at Babylon. It is evidence of the largely nomadic population living on the banks of the Uzboy. The period from 7th c. BC to 5th c. AD was flourishing for Aral-Caspian area, combining settled agricultural and tribes specializing in sheep or horse animal husbandry. A symbiosis of farmers and nomads. | |
| 500 BC | Indian sources identify Alans-Ases as Jats called Asiaghs and relate that Assyria was called after the Asiagh Jats. The Asii Jats founded Jutland as their homeland in Scandinavia. Scandinavian “Edda” tells that ancient inhabitant of Scandinavia were Jats or Jits who were Asi people who came to that land from Asirgarh. Pliny relayed that Sindhu Jats from Sindh were called upon during a conflict between Anatolia and Babylonia. They belonged to Hasti dynasty. Asiagh Jats ruled Alexandria in Egypt. Their title was Asii. | |
| 300 BC | From Chinese sources, Alans are listed as one of four Hunnish tribes (Xu-la, Lan, Hiu-bu, Siu-lin) most favoured by kings of Eastern Huns (Mao-dun/Mete and his son Ki-ok/Kök) of 3rd century B.C. (ToOD 146). Hiu-bu and Siu-lin are Ch. coding variations for Yui tribes, Uigurs; Lan stands for Alan = Tr. alan, yalan = steppe, synonymous with Tr. yaziq = plain, plateau (Yazygs, Ases, Yases). Alt. name for Alans (probably, a W.Europe subtribe) is Gu-alan, Tr. quw alan = dry steppe; both names indicate part of clans living in steppe, while other part lives by river, mountain, forest etc. 1 | |
| 220 BC | End 3rd c. BC Earliest notable Sarmatian migration to Scythia. | |
| 210 BC | ca 310- 100 BC Second, largest stage of Sarmatian migration to Scythia, ended with the crush of Scyths and Sarmatian dominance in N.Pontic. | |
| 204 BC | HUN EMPIRE 204 B.C – 216 A.D Area – At north, Siberia; south, Tibet – Kashmir; east, Pacific Ocean; west, Caspian Sea; (Total Area – 18,000,000 Km 2) Founder – Mete (Bagatir, Maotun, Batur) of Suy-Lyanti clan with a bull totem establishes Hunnic Empire. | |
| 107 BC | The first historical appearance of Rhoxolani, between Dnieper and Don: Tasius, leader of Rhoxolani, an ally of Palacus, King of Crimean Scythians, against Mithridates VI Eupator, King of Pontus. | |
| 64 BC | 64/47 B.C. The first historical appearance of Aorsi, between Don and North-West of Caspian Sea: Spadines, King of Aorsi at time of Pharnaces, King of Bosporus. | |
| 48 BC | WESTERN HUN EMPIRE 48 BC – 216 A.D Founder – Panu Area – an area over present Central Asia. | |
| 16 BC | Consul Lucius Rufus repulsed the first attack of Iazyges on Moesia. | |
| 6 | Iazyges and Dacians again attacked Moesia. | |
| 35 | 35-36 AD Alan participation in Ibero-Parthian (Artabanus II) war on side of Iberia. | |
| 49 | Eunones, King of Aorsi, an ally of Romans and of Cotys I, King of Bosporus, against Mithridates, latter’s brother. | |
| 50 | Iazyges are noted on Tissa plain. | |
| 50 | Farzoy’s empire formed in Middle Dniester | |
| 56 | 56-63 Plautius Sylvanus repulsed the onslaught of Sarmatians on Lower Danube. | |
| 60 | 60/67 Embassy to ”Greatest Kings of Aorsia”, perhaps from Olbia. | |
| 62 | Vologeses inscription: Parthian king Vologeses (51–80AD) in his 11th year battled Kuluk (Külük ), king of Alani. | |
| 67 | 67-68 Roxolans devastated Moesia. | |
| 69 | Rhoxolan raid against Moesia checked by Third Legion of Mark Antonius. | |
| 69 | Roxolans in alliance with Dacians again attacked Moesia. Farzoy resumes minting of gold coins. | |
| 72 | Alans invade S.Caucasus. Külük defeated Medians and Armenians in a raid south. | |
| 72 | Alan raid against Parthian vassal kingdoms of Media and Armenia. | |
| 75 | In the area between Dniester and Prut appeared Roxolans and Aorses-Amakeobies. | |
| 89 | 89-92 Iazyges together with German tribe Suebi attacked Domitian, who suffered a crushing defeat. This is the first successful attack of barbarians against the empire. | |
| 93 | 93/123Possible alliance between local Barbarian chieftains and Alans at time of Sauromates I, King of Bosporus. | |
| 102 | Roxolan cavalry participates in Decibal’s raid to Lower Moesia. | |
| 117 | 117-118 Roxolans from E., Yazygs from W., attack Roman Dacia. | |
| 117 | 117/38 Sarmatian and Rhoxolan raids in Moesia under Hadrian. Peace with king of Rhoxolani, probably P. Aelius Rasparaganus. | |
| 124 | Dionysius Periegetes (the Guide) Orbis terrae descriptio map showing Huns (Unni), Caspii, Massagets, Sacii, Alani, Scyths, Hyrcanii, Sarmats, Taurii. | |
| 128 | Tacitus: Emperor Hadrian (117-138 AD) pays Rhoxolani annual tribute and allows their transit by the Roman roads through Dacia with Iazyges, who lived along Tissa. | |
| 135 | Alan campaign in Transcaucasus and Media. Alan raid against Albania, Media, Armenia and Cappadocia, repelled by Flavius Arrianus of Nicomedia. | |
| 138 | 138/61 Alan raids under Antoninus Pius. | |
| 139 | Ptolemy (83?-161? AD) writes that in European Sarmatia ‘below Agathyrsi (Akatsirs, Tr. agach ers ‘forest people’) live Savari (Türkic Suvars), between Basternae and Rhoxolani (Tr. Uraksy Alans, i.e. ‘Alans-farmers’) live Huns. | |
| 150 | Hou Han shu: In China, Alans were earlier known as Yancai (奄蔡 ”Vast Steppe”). They have about 100,000 bowmen and same way of life and clothes as Kangju (Kangars) and identical with Ta Yüeh-chih (”Great Tochars”). Yancai changed its name to kingdom of Alanliao with capital Di. “Weishu” referring to 457: “Country of Sute (Sogdiana, with Samarkand) is situated west of Pamirs. In ancient times it was Yancai”. | |
| 150 | Hou Han shu: Alans are a dependency of Kangju (Tashkent plus the Chu, Talas, and middle Jaxartes basins). The climate is temperate. Wax trees, pines, and aconite are plentiful. | |
| 150 | Mid. 2nd century Alans defeated by the Roman army at Olbia. | |
| 160 | ca 160 First appearance of Alans in Lower Danube. | |
| 160 | Lucianus Samosatensis (ca 120-180AD) and scholia to Lucianus mention “barbaric Kona” in the east of Sarmatian lands around lower Danube, thought to refer to Kangars (see Besenyo Dateline). | |
| 161 | During the reign of Marcus Aurelius (161-180), Alans joined Sarmatian federation and Sarmatians became dangerous again. Romans had to fight several bloody wars against Sarmatians and their allies, Marcomanni. | |
| 167 | 167/80 Alans in Germanic wars of Marcus Aurelius. | |
| 167 | ca 167-175 First Markoman War. Markomans, Quads, Yazygs in Middle Danube, Roxolans, Alans, Costoboks and Free Dacians in Lower Danube. | |
| 175 | Marcus Aurelius defeats Iazyg tribe of Alans, takes 8000 into Roman service and himself settles with 5,500 of them in Northern Britain at Ribchester south of Lancaster. Alans were assigned to VI Legion Victrix commanded by Alani warlord who was renamed Lucius Artorius Castus. When these auxiliary cataphracts (heavy cavalrymen) retired from duty they were settled near the Lancashire village of Ribchester, known in Roman times as Bremetennacum Veteranorum. In 20th c population along Hadrian Wall records an elevated level of group B blood, 16% vs 8%. | |
| 178 | 178-180 Second Markoman war Dacia was attacked from by Markomans, Quads, Iazyges from the west, Roxolans, Carps, and free Dacians from the east., Alans etc from the north. | |
| 180 | Rhoxolani North of East Danube border shortly before the death of Marcus Aurelius. | |
| 178 | ca 178-180 Second Markoman War. Dacia is attacked by Markomans, Quads, Yazygs from W., Roxolans, Carpii, Free Dacians from E., Alans from N. | |
| 185 | 185/89 Alan raid against Mc’xet’a, capital of Iberia, intercepted by Georgian king Amzasp II. | |
| 193 | 193/208 Erakas, ”chief interpreter of Alans” at Panticapaeum. | |
| 210 | ca 210 Sarmatians (federated with Alans) occupied Dacia and from then on war against tribes on the north bank of Danube was really dangerous. | |
| 216 | End of HUN EMPIRE End of WESTERN HUN EMPIRE 204 B.C – 48 BC (split) – 216 A.D Area – At north, Siberia; south, Tibet – Kashmir; east, Pacific Ocean; west, Caspian Sea; (Total Area – 18,000,000 Km 2) Founder – Mete (Bagatir, Maotun, Batur). | |
| 216 | Western Hun Empire separates into 5 successor states (215-290) Tele (Gaogyuys). | |
| 225 | Hou Han shu: Alans were vassals of Kangju (Tashkent plus the Chu, Talas, and middle Jaxartes basins). Now they are no longer vassals. | |
| 225 | Alans allied with Armenian king Xosrov I against Persians. | |
| 230 | ca 230 Goths come to NW Pontic. Roxolans arrive at Tissa plain to Yazygs. Archeology finds Yazygs in utter poverty, their only supplies coming from Roxolans, from whom they were cut off for generations. Combined Roxolans and Yazygs are somewhat better off, but now they both are cut off from commerce. | |
| 235 | 235-38 Reign of Maximinus, supposedly of Alan descent. | |
| 238 | 238/44 Defeat of Gordianus III before Alans at Philippi. | |
| 242 | Alans allied with Goths and Carpi intrude Thrace and defeat Gordian II at Phyllipolys. | |
| 243 | 243/73 Expansion of area of influence of Sasanian Persia as far as ”Gate of Alans” (Darial) under Sabuhr I. | |
| 260 | Death of usurper Regalianus in Moesia, at request of Rhoxolani. | |
| 274 | Alans in triumph of Aurelian over Zenobia of Palmyra and Gallic usurper Esuvius Tetricus. | |
| 276 | 276/82 Skirmishes between Rome and Alans under Probus. | |
| 300 | by 300, Ammianus, XXXI, 2, 12: Alans ”by repeated victories incorporated under their own national name Geloni, Agathyrsi, Melanchlaeni, Anthropophagi, Amazons, and Seres”, showing a leadership of powerful state by Ammianus time. | |
| 300 | Goths subjugated Alans with their subjects reaching to Don on E. | |
| 330 | 330/38 Alans allied with Sanesan, king of ”Massagetae” (Mazk’owtk’), against Armenian king Xosrov II Kotak 330’s King Sanesan of Maskuts/Masguts/Massagets ~ Sanatruk (Truk ~ Türkic) ruler of Paitakaran (~Bai Tarhanlyk). | |
| 351 | 351/67 Alans allied with Armenian king Arsak II against Persians. | |
| 354 | Earliest known European record about Bulgarians is “Anonymous chronograph“, a list of tribes and peoples in Latin. He mentions a certain ‘Ziezi ex quo Vulgares’. | |
| 356 | 356/7 Shapur II repulses Chionite Huns on border of Persia. | |
| 359 | Chionite King Grumbat took part in siege of Amida as federati of Persian Shah Shapur II. | |
| 360 | Huns cross Volga and attack Alans. Part of Alans retreat to N. Caucasus, part is absorbed in Huns Horde, part retreat to N. Donets. Most likely, after conquest a part of Bulgars joins Huns, and a part remains. | |
| 360 | Jordanes: With approach of Huns Alans revolt against Goths, helping Huns to move against Ostrogoths under Ermanaric. Alans concluded concordia with Huns to move against Ermanaric under unknown terms of alliance. | |
| 360 | Hunno-Alanic alliance guaranteed Alan partner considerable degree of independence and large share of loot. Alans are part of Hunnic confederation (ca 360-398). | |
| 370 | 370-376 War between Alans and Goths. | |
| 370 | Huns control N. Pontic, Tanais and N. Caspian steppes. Living there Alans join Huns. | |
| 371 | Huns invade Goths’ possessions in N.Pontic. | |
| 372 | Don Alans crushed by Huns. Part of Alans joins Huns to Europe. | |
| 375 | EUROPEAN HUN EMPIRE 375 – 454 A.D Founder – brothers Muncuk, Oktar, Rua & Aybars Area – S Russia, Romania, N Yugoslavia, Hungary, Austria, Chekoslovakia, S& C Germany. From E France to Urals; from N.Hungary to Byzantine Empire (Area – 4,000,000 Km2). | |
| 375 | Ammianus Marcellinus bk. XXXI, 12 considers Alans to be descendents of Masguts (Massagets). | |
| 375 | Battle between Alans under Bülümar (Jordanes, XLVIII, 249) and Ostrogoths at river Erac (present Tiligul). After death of Vitimir young Vidirix bacame a King. Alatei and Safrac ruled under his name. Both names Alatei and Safrac sound more Türkic then Germanic, they may be Hun’s viceroys. Ostrogoths retreated to Dniester. | |
| 375 | Ammianus Marcellinus: ”After his (Hermanaric) departure, Vitimir was made a King, and resisted Halans for some time… But after many defeats he suffered, he was subdued by arms and died in battle”. | |
| 375 | 375-383 Alans serve in Gratian’s guards. Alania in Lower Danube. | |
| 375 | Subjection of Alans by Huns, Destruction of Ostrogothic realm of Ermanaric by Huns and Alans. | |
| 376 | Huns captured Atel-Kuzu (Bessarabia). Alans remained in Dacia. Vestgoths and Ostrogoths, defeated by Huns and Alans, retreated to Danube. | |
| 376 | With Ermanaric’s Ostrogoths, Hun’s Bülümar (Balamber) acquired not only Alans, but other Ostrogoth subjects. Jordanes: ”thirteen peoples which the Amalung ruler Ermanaric conquered in north: Golthescytha (Goths Scyths), Thiudos (Germ. People), Inaunxis?, Vasinabroncae?, Merens (Merya,), Mordens (Mordvins), Imniscaris?, Rogas (Germ.), Tadzans?, Athaul (Türk. Atagul=Archers), Navego?, Bubegenes?, Coldas”, plus Heruli, Aesti (Ests, Estonians) and Venethi, numerous people Taifali who before 370 held Oltenia and western part of Muntenia. In Gaul Taifali, probably Türkic, and Sarmatians were settled together. | |
| 376 | Huns and Alans appeared in Pannonia. | |
| 377 | 377/8 Alliance of Huns and Alans with XXX or Barbarians in Moesia. | |
| 377 | Ammianus: Romans had their Saracen horses. This is before Kumans=Kipchaks show up under a name Saracen by 500 years. Ptolemy’s Geography refers to distinct from Arabs Σαρακηνός Sarakenoi people in north-western Arabian peninsula. | |
| 377 | Romans cornered Visigoths against Danube, and Ammianus stresses that number of Huns and Alans was small, but threatening rear of Romans, they removed Roman siege. Strategic move on such scale required more than agreement between Visigoths and Huns. Very first account of Hun raid into Balkan provinces shows their cohesion and abilities. | |
| 378 | Oldest son of Hun’s Bulyumar (Balamber) Alyp-bi defeats Sadums (Goths/Scandinavians), crossed Danube and with Visigoths, Ostrogoths and Alans defeats 80K Byzantium army at Andrianopole. Precise maneuvering and overreaching encirclement of Roman forces and supplies by Huns and Alans shows immaculately coordinated strategic campaign. | |
| 378 | Valeria, the easternmost province of Pannonia, overrun by Goths, Huns, and Alans. | |
| 378 | Visigoths overrun Taifali in Oltenia, and Sarmatae Limigantes, the ”slaves” of Sarmatae Argaragantes, join Visigoths sent by Huns to capture Banat (Caucaland), turned against their Argaragante lords. Pannonia Sarmats join Huns. | |
| 378 | Gratian, attacked by Alans in Pannonia. Alans in army of Fritigern, king of Visigoths, in battle of Adrianople (Aug. 9th). Defeat and death of Emperor Valens. Raids by Goths, Huns and Alans as far as Constantinople. | |
| 379 | Victories of Emperor Theoodosius over Alans, Huns and Goths. | |
| 380 | New Roman Emperor Theodosius settles Gothic problem diplomatically. Goths become federates, and Alans move north. | |
| 380 | 380-395 Alans clear Dacia and Bessarabia from Vestgoths, Taifals, Gepids, Burgunds and other peoples. Huns went to Pontic steppes. | |
| 380 | Recruitment of Alans into Roman army by Gratian. Settling of Alan, Hun and Gothic auxiliary troops in Pannonia by Theodosius. | |
| 383 | 383/4Alan and Hun auxiliary troops called on by Frankish magister militum Bauto against Juthungi in Raetiae. | |
| 390 | Ethnographic excursus on Alans by historian Ammianus Marcellinus. | |
| 394 | Saul, general of Theodosius’ Alan auxiliary troops in battle of River Frigidus against Arbogast and usurper Flavius Eugenius. | |
| 395 | Hun campaign in Transcaucasus and even raid Syria (Caucasus, Syria, Cappadocia, and Mesopotamia ). Alans, Ostrogoths and Geruls, retreated earlier to Transcaucasus, subordinate to Huns. | |
| 398 | Alan auxiliary troops in Norrn Italy. | |
| 400 | Alans and Bolgars live between Itil and Don. | |
| 401 | 401/10Alans in army of Visigothic king Alaric in Norrn Italy. | |
| 402 | Ruler of Western Empire Stilihon allied with Huns and Alans, who help Stilihon to fight off attack of German tribes. | |
| 402 | Alan auxiliary troops in Stilicho’s army in battle of Pollentia against Alaric. Internecine strife between Alans and Huns (location unknown). | |
| 402 | Orosius: between federates in Roman service after 402… ”I say nothing of the many internecine conflicts, when two cunei of Goths, and then Alans and Huns, destroyed one another in mutual slaughter”. | |
| 402 | Hunnic noblemen, Attila’s relatives and retainers, have either Turkish or Germanic names. There evidently were few, if any, Alans among leading group. | |
| 405 | New help by Huns and Alans to Stilihon to fight off attack of German tribes (Sweves). | |
| 405 | Alan and Hun auxiliary troops in army led by Stilicho against Ostrogothic king Radagaisus. | |
| 406 | Alans join Vandals in invasion to Gallia (modern France). Migration of Pannonia Alans and Vandals to Gaul. | |
| 406 | Crossing of Rhine by Vandal king Godigisel and Alan king Respendial. Battle against Prankish foederati in Roman service (Dec.31st). Earlier defection of Alan Goar. | |
| 406 | Disintegration of Hun’s confederation: Alans left Huns. From 360 to 398 Huns and Alans are constantly named together, Huns mostly, though not always, in first place. In 394 only transdanubian Alans, led by Saul, joined Emperor Theodosius; of the Huns only those in Thrace marched under imperial dragons. Alans, but no Huns, served Stilicho in 398 and, still under Saul, in 402. In 406, however, Stilicho’s barbarian auxiliaries consisted of Huns and Goths; his bodyguard was formed by Huns. Huns, but no Alans, served in the Roman army in 409. | |
| 406 | After 406, Western writers knew of Alans only in Gaul, Spain, and Africa. No author of fifth century mentions Alans as allies of Huns. | |
| 407 | Alans settled extensively north of Loire river, once called Armorica, now called Brittany. Alans arrived at about same time as Celtic Britons were fleeing to France after Saxon takeover of England. Alans and Celtic Britons intermarried extensively. Legacy of Alans includes French name ”Alain” and its many variations, and cultural foundation of chivalric warfare (armored knights on horseback) =>see 436. | |
| 407 | Invasion of Gaul by Alans, Suebi and Vandals. | |
| 409 | Alans and Vandals moving from Gallia to Spain. | |
| 409 | Part of Alans, with Respendial at helm, intruded into Pyrenean peninsula, where they formed Alanian state. Captured lands were shared between Alans and German tribes of Vandals and Svevs taking part in the invasion. | |
| 409 | Invasion of Spain by Alans, Suebi and Vandals. | |
| 410 | Alania in Lower Danube. | |
| 410 | Bulgars attack Lombards (Longobards). | |
| 411 | Goar (Goarchur) (?- 415) leads Alans who abandoned his Vandal allies. | |
| 411 | Dividing up of Spain among invaders: Alans, lords of Lusitania and Carthaginiensis. Failed attempt at an agreement with Emperor Honorius. | |
| 411 | Alans in service of Gerontius, magister milltum of usurper Maximus in Tarraco. | |
| 411 | Proclamation of usurper Jovinus in Mundiacum (Germania Secunda) by Alan Goar and Burgundian Gunthiarius. | |
| 412 | Byzantine Embassy to Western Huns in Pontic area. | |
| 414 | Defection of Alans allied to Visigoths during siege of Vasatae (Aquitaine). | |
| 415 | Attaces (Addak) (415 – 426) Alanian King killed in battle against the Visigoths. | |
| 416 | Alans were followed into Spain by numerous tribes of Westgoths. | |
| 416 | 416/7 Campaigns led by Vallia, king of Visigoths, against Alans and Vandals in Spain. | |
| 418 | Westgoths defeated Alans. Alanian Chief Addak perished in combat. With his doom Alanian state on Pirenean peninsula ceased to exist. From this we can see a possible explanation how ht35 haplotype may have arrived in Spain and subsequently in Spanish Netherlands, which may be of interest in evaluating the DYS393=12 allele. | |
| 418 | Addac, king of Alans in Spain, defeated and killed by Vallia, perhaps at Gibraltar (”in Tartessian lands”). Submission of surviving Alans to Gunderic, king of Asding Vandals in Gallaecia. | |
| 418 | Alans in 418 subjugated themselves to the patrocinium of the Vandal king, they retained their tribal organization until the end of Vandal kingdom. | |
| 420 | Huns occupied Pannonia. Western Huns settle in middle Danube. Rulers were Yabgu Roila (Rugila), Aybat (Eur. Mundzuk) and Kagan Oktar. | |
| 422 | Byzantine peace treaty with Persia. | |
| 424 | 424-71 Activity and pre-eminence of family of Alan Flavius Ardabur Aspar in Byzantium. | |
| 428 | 428-77 Geiseric, King of Vandals and Alans. Orga nization of Vandal army in chiliarchies. | |
| 429 | Crossing of Vandals and Alans from Spain to North Africa. | |
| 434 | Huns siege Constantinople. Death of Rugila. Beginning of joint rule by Atilla and Bleda. | |
| 436 | St. Germanus pleads with Alanic King to spare Armoricans. Alans begin to settle in Armorica =>see 407. | |
| 440 | Settling in Valence of Alans under chieftain Sambida. | |
| 442 | Settling of Alans in Transalpine Gaul by Aetius. | |
| 445 | Beginning of Attila sole reign Attila’s 8 years overshadowed previous and following centuries in memory of Romans . | |
| 447 | 447/8 Eochar, king of Alans, sent by Aetius against Bacaudae of Armorica as a reprisal for their revolt, and stopped by St. Germanus, bishop of Auxerre. | |
| 448 | Attila’s defeat of Akatsir Scythians and appointment of Ellak as ruler of Pontus Huns. Eastern Roman ambassadors in Attila’s camp. | |
| 450 | Lazar Parbetsi: Allied armies of S.Caucasian countries capture fortifications named “pahane Honsü“ (defense against Hons) Destruction of Chor (future Derbent) fortress by rebellious Armenians and Albanians. | |
| 450 | 450/60 Expedition of Georgian king Vaxtang Gorgasali against Alans. | |
| 451 | 451.06.15 ”Battle of Peoples” at Catalaun ravine near present Trua. On Atilla’s side are Huns, Geruls, and part of Franks Ostrogoths, on Aecius side Roman legions recruited from Gaul and Germany, Vestgoths, Burgunds, Franks, Armorician Alans headed by Sanhiban. No definite result. | |
| 451 | Sangiban, king of Alans in Orleans, ally of Aetius and Visigothic king Theodoric in battle of Catalaunian Fields against Attila, king of Huns. | |
| 452 | Huns invasion in Azerbaijan. | |
| 453 | Subjection of [part of] Alans in [Transalpine] Gaul by Visigothic king Thorismud. | |
| 454 | Jordanes: You could see Goth with lances, Gepids with mad with sword, Rug breaking spears in his wounds, and Swev bravely acting with bat, and Hun with arrow, Alan with heavy, Gerule with light weapons. | |
| 454 | Atilla’s son Ellak tried to suppress rebellion, was defeated and died in battle at Nedao. Remains of Ellak’s army retreated east of Carpathians. Two other sons Dengizik and Ernak remained in Dacia and Bessarabia. Alans, led by ruler Kandak were forced to go to Dobrudja. | |
| 454 | End of EUROPEAN HUN EMPIRE 275 – 454 A.D Founder – brothers Muncuk, Oktar, Rua & Aybars Area – S Russia, Romania, N Yugoslavia, Hungary, Austria, Chekoslovakia, S& C Germany. From E France to Urals; from N.Hungary to Byzantine Empire (Area – 4,000,000 Km2). | |
| 455 | Alans in battle at Nedao River (Pannonia) between Ardaric, king of Gepids, and sons of Attila. Later settling in Scythia Minor and Lower Moesia of Alan chieftain Candac. | |
| 455 | Abdaly (Hephthalites) conquer Kushans and invade India. | |
| 456 | Byzantine captures Lazika. | |
| 457 | “Weishu” referring to 457: “Country of Sute (Sogdiana, with Samarkand) is situated west of Pamirs. In ancient times it was Yancai. It is also called Wennasha. It lies on an extensive swamp northwest of Kangju (Kangar). It is 16,000 li distant from Dai. Formerly, the Xiongnu (Eastern Huns) killed their king and took their country. King Huni was third ruler of the line”. | |
| 458 | Alan auxiliary troops in Majorian’s army. | |
| 463 | Saragurs subjugate Akatsirs. | |
| 464 | Beorgor, king of Alans, defeated and killed at Bergamo by patrician Ricimer (Feb. 6th). | |
| 466 | Invasion of Saragurs and Onogurs in Transcaucasia. | |
| 468 | 468 – 469 Danube war between Huns and Byzantium. Bel-Kermek (Hernach) after Dengizik death leads army. Byzantium beats off invasion with difficulty. Byzantium mercenary army consists of Slavs and Alans commanded by Aspar, whose father was Alan. | |
| 468 | ”in some respect Danube war of 468 – 469 was a war of Alans and Ants against their former masters, Huns.” (G.V.Vernadsky). After Byzantian victory Huns left Dacia and Bessarabia. These provinces opened for Slavic colonization. | |
| 468 | Huns offer alliance to East Roman empire. | |
| 469 | Death of Dengizih (Diggiz). | |
| 477 | 477-84 Huneric, King of Vandals and Alans. | |
| 478 | Attempted murder of consul Illus, counselor of Emperor Zeno, by an Alan. | |
| 481 | Goths’ Theodoric, son of Triariya, victory over Bulgars. | |
| 487 | 487/8 Expedition from Ravenna against Rugi led by Scirian king Odoacer with an army of Alans. | |
| 530 | 530-33 Gelimer, King of Vandals and Alans. | |
| 531 | 531/78 Foundation of Darband and fortification of Eastern and Central Caucasus by Sasanian king Husrav Anosruvan against incursions of Northern nomads. Creation of March of Alans. | |
| 534 | Destruction of Vandal kingdom of Africa by Belisarius. | |
| 548 | Alliance made by Gubazes, king of Lazi, with Alans and Sabirs against Iberia at time subjected to Sasanian Persia. | |
| 549 | Alans in expedition of Sasanian general Chorianes (Farroxan) against Lazica. | |
| 550 | Mid. 6th century. Period of king Sarosius’ government in Alania. Establishment of tight contacts between Alania and Byzanthia. | |
| 550 | Geographical description of Caucasus by Procopius of Caesarea. | |
| 551 | Zachariah Ritor: Bulgars and Alans are mentioned once as settled populations with towns, and once as nomads. He points that Bulgarian towns, inhabited lands are immediately next to Caspian gates, while nomads are in steppes north of Caucasus. | |
| 551 | Z. Ritor: ”Thirteen peoples Avnagur (Onogur), Avgar, Sabir, Burgar, Alan, Kurtargar, Avar, Hasar, Dirmar, Sirurgur, Bagrasir, Kulas, Abdel and Hephtalite live in tents, earn their living on meat of livestock and fish, of wild animals and by their weapons”. | |
| 552 | GOKTÜRK Kaganate 552 – 743 A.D Founder – Bumin Khan (Tumen) Area – From Black Sea across Asia along northern borders of Mongolia and China almost to Pacific Ocean, and valleys of Altay Mountains (Ergenikon) (Total Area – 18,000,000 Km 2). | |
| 555 | Description of Caucasus by Pseudo-Zacharias Rhetor. | |
| 556 | Possible territorial conflicts between Alans and Misimians, subjects of king of Lazica. | |
| 557 | Arrival of Avars in land of Sarosius (Sarodius, Saroes), king of Alans. | |
| 558 | Gumilev: Vars (Ugrian tribe, related to Hungarian ancestors Ogors/Ugrs which lived between Itil and Ural rivers, and to Hungarians living in Bashkiria up to XIII c.) and Huni (Khionites = Sarmato-Alanians), both from North of Aral Sea, become known as Avars. | |
| 561 | Fifty years peace between Justinian and Husrav Anosruvan. Alans and Huns forbidden to cross Darial and Darband to attack Byzantine territory. | |
| 563 | In 563-567 Persians run successful military actions against Ephtalites, to about same time belongs defeat by Khosrow Anushirvan of Savir tribes residing in S.Caucasus. Savirs lived in the plains N. and S. of Derbend, Southern Savirs lived next to or interspersed with Masguts (Alans). | |
| 566 | Between 566 and 571 Istemi Djabgu subjugated peoples Banajar, Balanjar (Belenjer) and Khazar. Baranjar (Balanjar) = Onogur = Utigur Bolgars. Khazar influence increased as Khazars became Turks closest allies and assistants. | |
| 569 | 569-571/2 Embassy of Zemarchus to Khanate of Western Turks. Persian attempt to intercept Zemarchus through Alans. On way back, tension between Sarodius, king of Alans, and Turkic ambassadors. | |
| 572 | Saroes, king of Alans, ally of John, strategos of Armenia, against Persians. | |
| 574 | 574/78 Alans (allies of Persians) captured and taken as hostages to Byzantium under Tiberius Constantine. | |
| 576 | Byzantine foray into Sassanid-controlled Albania, Byzantine generals Kurs and Theodor relocated Albanian Savirs and Alans on other sode of Kura. Beginning of Alan control of Daryal Pass, it becomes Alan Pass. | |
| 576 | Possible subjection of [part of] Alans by Western Turks. | |
| 580 | Incursion of Alans in pay of Byzantium against Persian Azerbaijan. | |
| 581 | “Sui shu“ (581 to 618) chapter 84 “Description Of Tele“ lists 45 tribes of Asian steppe, including a-lan (Alans). Alans are included in listing of Turkic-speaking Tele tribes. | |
| 642 | Campaign of Hudaifa b. Asid (Asad), general of Caliph ‘Umar I, in mountains of Alans. Fortification of passes of Central Caucasus by Arabs. | |
| 651 | With loss of W.Khaganate rule, former confedrate Khazaria with attached Bolgar Kutugurs, Alans, Slavs and Itil Bolgars gain independence. Khazars keep Khagan from dynasty Ashina. | |
| 651 | Defeat of Khazar-Alan army by Abd Al Rahman Arabs in Euphrates battle. | |
| 655 | Gumilev: Khazars cooperate with Iranian speaking Alans. | |
| 662 | 662/3 Muslim expedition against Alans. | |
| 670 | Bat-Boyan Bolgars are defeated by Khazars. Khazars recover territory with east Bolgar (Utugur) and Alan populations. | |
| 682 | Albanian missionary bishop Israel describes ”Kingdom of Huns” (Belenjer) capital Varachan located north of Derbent, and Tangri cult of Northern Dagestan Baranjar (Balanjar) = Onogur = Utigur Bolgars, subordinated to Khazars. | |
| 705 | 705/15 Adventures of spatharius Leo (future Emperor Leo III) in Caucasus. Alan raids against Abasgia (under Arab rule) instigated by Justinian II. | |
| 715 | 715/20 Arab expedition against Alans under Caliph ‘Umar II | |
| 721 | 721/2 Invasion of country of Alans by Turks (Khazars). | |
| 722 | Second Khazar – Arab war (722-737) First campaign of Arabian troops led by Zh. Jirrah in Northern Caucasus against Alans and Khazars. | |
| 722 | 722/3 Defeat of Arab general Tabit al-Nahram by Alans and Khazars. | |
| 723 | Khazars lose Balanjar to Arabs, move capital to Samandar. | |
| 723 | 723/4 Expedition against Alans and Khazars led by al Jarrah b. ‘Abdallah al-Hakami. | |
| 724 | 724/5 Alans, tributary people to Umayyad Caliphate as a result of expedition against them led by al-Hajjaj b. ‘Abd al-Malik. | |
| 728 | 728/9 Expedition against Turks (Khazars) led by Maslamah b. ‘Abd al-Malik through Gate of Alans (Darial). | |
| 730 | 730/1 Defeat and death of al-Jarrah b. ‘Abdallah al Hakami at hands of Turkic (Khazar) invaders from country of Alans. | |
| 735 | Campaign of Arabian military leader Mervan Kru in Alania. Alanian king Itaz. | |
| 735 | 735/6 Conquest of three fortresses in country of Alans by Marwan b. Muhammad. | |
| 737 | 737/8 Expedition against country of Khazars led by Marwan b. Muhammad through Gate of Alans. | |
| 751 | Alan auxiliary troops in Armenia serving in army of Constantine V. | |
| 758 | Conquest of Gate of Alans by Yazid b. Usayd b. Sulami. | |
| 770 | Oguzes came to Transoxania in 770’s. | |
| 772 | War between Greeks and Bulgars. Khazaria unites with Alania. | |
| 776 | St. Beat map between estuaries of Danube and Dniester shows country Alania. | |
| 820 | 820/23 Alans in army of Thomas Slav, leader of revolt against Byzantine Emperor Michael II. | |
| 842 | 842/47 Travel of Sallam, interpreter to court of king of Khazars, through country of Alans. | |
| 851 | 851/2 Expedition of Turk Abu Musa Buga Elder against Georgians, Abkhaz, Alans and Khazars. One hundred Alan households deported to Dmanisi (Tasiri). | |
| 888 | 888-907–Alan I the Great, King of Brittany. | |
| 888 | 888/923 Alan Baqat’ar, ally of Bagrat I of Abkhazia against Georgian king Adarnase II. | |
| 895 | Alans and Bulgars freed from Khazar power. | |
| 900 | Alano-Khazar war during reign of Aaron, king of Khazaria. | |
| 903 | 903/13 Geographical description of kingdom of Alania by Ibn Rustah. | |
| 905 | 905/15 Conversion of king of Alans to Christianity through intercession of exusiastes of Abasgia. Beginning of mission of Peter, Archbishop of Alania. | |
| 910 | First missions of Christian preachers from Byzantine to Alania. Establishing Alan arch-episcopate. Peter a first arch-bishop of Alania. | |
| 920 | Khazars fight with Burtas (Steppe Alans or As), Oghuz, Byzantines, Kengeres and Kara Bolgars. | |
| 924 | Attempt at an anti-Bulgarian alliance by Emperor Romanus I Lecapenus with Ruses, Pechenegs, Alans and Magyars. | |
| 930 | Khazars ally with Alans who adopt Judaism, and arrange a dynastic marriage. | |
| 931 | Christian religion abjured by Alans. Expulsion of bishops and priests sent by Byzantine Emperor. | |
| 943 | 943/56 Geographical description of kingdom of Alania by al-Mas’udi. First recorded appearance of its capital city, Magas. Alliance between king of Alans and king of Daghestan Avars. | |
| 943 | Al-Masoudi ”Meadows of gold and mines of precious stones”: ”King of Alans furnishes 30,000 cavalry … He is a powerful king, strong, and he enjoys more influence than other kings”. By that account, at ca 900 AD Alania has 150,000 population. | |
| 944 | 944/5 Incursion of Alans, Russians and Lesghians against Arran. | |
| 945 | 945/59 First recorded appearance of exusiocrator of Alania (dated during reign and literary activity of Constantine Porphyrogenitus). | |
| 965 | Destruction of Khazar Empire and defeat of Alans and Circassians by Rus prince Svyatoslav of Kyiv. | |
| 977 | Ibn Haukal in the ”Face of the Earth” records that Azeri and Persian languages were being used as Lingua Franca across the Caucasus. | |
| 1014 | 1014/27 Alda, Alan princess, wife of Giorgi I of Georgia. | |
| 1029 | Death of Urdure, king of Alans, slain in battle by Kwirike III, king of Kaxet’i. | |
| 1029 | Expedition led by prince Yaroslav Wise of Kyiv against Alans. | |
| 1032 | 1032-33 Failed incursions of Alans, Avars and Ruses against Muslim city-states of Sarwan and Darband, in East Transcaucasia. | |
| 1050 | 1050/55 Love affair between Emperor Constantine IX Monomachus and a daughter of king of Alania. | |
| 1062 | 1062/65 Alan raids through Darial against Saddadid emirate of Arran (East Transcaucasia). Dorgoleli, king of Alans. Marriage of Georgian king Bagrat IV with Alan princess Borena. | |
| 1065 | Visit of Alanian king Durguleit Great to Georgian king Bagrat IV in Kutais. | |
| 1066 | Many Bretons of Alanic ancestry joined William The Conqueror in the conquest of Britain, contributing military tactics inherited from their forebears, and later spread their genetic influence across Britain into Scotland and elsewhere. One of the highest frequencies of R1b Haplotype 35 anywhere in the Y-STR database is among sample from Paris, France, adjacent to Normandy, and even more so, among Americans of ”Cajun” descent. ”Cajun” is actually a colloquial contraction of the word ”Acadian” (now Nova Scotia and New Brunswick, and portions of northern Maine). Majority of early French Canadian settlers of both Acadia and Quebec were of Norman or Breton origin. Many Scottish families who exhibit DYS393=12 marker are as likely to be descended from the Alans who arrived with the Normans, as from the Sarmatians who came with the Romans. | |
| 1072 | Marriage of Maria of Alania with Byzantine emperor Michael VII Duca Parapinaces (1071-1078 d. 1078). Marriage of Georgian king George III with Alanian princess Burduhan. | |
| 1072 | 1072/75 Recruitment of mercenary troops in Alania by Michael VII Ducas in order to face revolt of Norman Roussel of Bailleul. Alan mercenaries in service of Comneni brothers in Anatolia. | |
| 1075 | 1075/95 Intrigues in Byzantium of Maria of Alania, wife of Michael VII Ducas and Nicephorus III Botaneiates. Irene of Alania, wife of Sebastocrator Isaac Comnenus. | |
| 1085 | Adam of Bremen (ca 1050-1085) described ancient Scythian tribes in eastern Baltic region, pointed out: “‘There live Alans or Albans, who in their own language are called Vizzes. The last are very cruel Ambrones born with white hair”. (Vizzes/Wizzes could be Vizigoths,or Türkic bizə with semantics of “painted”, e.g. Acathyrsi-type or Issyk kurgan or Pazyryk-type tatoo). | |
| 1089 | King of Ovs (As, Alans) David Soslan’s son marries Queen Tamar. | |
| 1099 | Formation of Karachai-Balkarian (Alan) people completed. | |
| 1107 | 1107/8 Rhosmices, exusiocrator of Alania, in service of Byzantines during invasion of Epirus by Norman prince Bohemund of Antioch. | |
| 1116 | Don Kipchaks are again invaded and defeated by Russian Princes. Cities Sharukhan, Sugrov and Balin with Alano-Bulgar populations are taken. | |
| 1116 | Rus expedition against Cumans. Marriage of Yaropolk, son of Vladimir II Monomah of Kyiv, to Alan princess. | |
| 1116 | Alan mercenaries in army recruited by Alexius I Comnenus to face Turks of Seljuq Sultan Melik Shah. | |
| 1118 | Kipchaks make peace with Alans. Khan Otrak has 40K army and is allied with Georgian King David IV the Builder, and participates in war with Seljuks. Many Kipchaks settle in Georgia. | |
| 1130 | Abu Hamid al-Garnatfs stay in Darband. | |
| 1150 | Khuddan, king of Alans. Marriage of Georgian prince Giorgi to Alan princess Burdukhan. | |
| 1150 | Hieronim’s map names Danube tributary r. Pruth ”Alanus”. | |
| 1153 | Ibn al-Azraq’s journey to Alania together with Georgian king Demetre I. | |
| 1155 | 1155/6 Alan mercenaries in expedition to re-conquer Italy sent by Emperor Manuel I Comnenus. | |
| 1160 | 1160/73 Benjamin of Tudela’s journeys. Evidence for Jewish communities in Alania. | |
| 1173 | 1173/4 Incursion of Alans, Ruses, Cumans and Avars in service of Bekbars of Darband against Sirwansah Ahsatan b. Manucehr. | |
| 1175 | Brother of the ”Yasian Princess” (brother-in-law of Prince) Alanian majordomo Küchük Anbal (Turk. ”small” + ”son of concubine”) killed Prince A. Bogolubsky. | |
| 1184 | 1184/1212 Marriage of Georgian queen T’amar with Alan Davit Soslan. | |
| 1185 | Alan mercenaries in defence and reconquest of Thessalonica against Normans of Sicily. | |
| 1189 | Annihilation of a corps of Alan mercenaries near Philippopolis (Plovdiv) by crusaders of German Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa. | |
| 1222 | Defeat of Alans and Kipchaks in first fight against Mongol-Tatars. Mongol-Tatars seizing capital of Alania Magas (Meget). | |
| 1222 | First Mongol expedition against Caucasus: defeat of Alans and Cumans. | |
| 1225 | 1225/30 Alans in service of Georgian queen Rusudan against invasion of Hwarezmsah Galal al-Din. | |
| 1226 | 1226/40 Pastoral journey of bishop Theodore to metropolitan see of Alania. | |
| 1229 | 1229/59 Subjection and transfer to China of Alan families by Mongols during reigns of Ogodei and Mongke. | |
| 1236 | 1236/7 Qachir-Ukule, amir of Ases, captured and executed by Mongke on shores of Volga. | |
| 1239 | Annexation of Alania into Ulus Juchi. | |
| 1239 | 1239/40 Alans and their capital *Magas conquered by Mongols. | |
| 1243 | 1243/69 Marriage of Georgian king Davit VII Ulu (Turk. ”David Uĝlu = Great”) to Alan [princess?] named Altun (Turk. ”Gold”). | |
| 1245 | 1245/55 Reported resistance to Mongols by part of Alans in the Caucasus. | |
| 1253 | 1253/55 Journey of Friar William of Rubruck to Mongol Empire. Alans in Qara Qorum. | |
| 1258 | 1258/1368 Military activity of Alan mercenaries in service of Mongol Yuan dynasty in China. | |
| 1261 | Diplomatic relations between Mamluk Sultan al-Malik al-Zahir and Berke, Khan of Kipchak Khanate, through Alan merchants. | |
| 1263 | 1263/64 Reported Alan settlements in Crimea. | |
| 1275 | Massacre of a garrison of [Christian] Alans in service of Mongol general Bayan in the Chinese city of Zhenchao (Jiangsu). | |
| 1277 | 1277/78 Expedition of Rus princes against Alans sent by Khan of Kipchak Khanate Mongke Termir. | |
| 1278 | Mongol-Tatars and Ruses seize Alanian town Dediakov. | |
| 1280 | 1280/1300 Alans in service of Mongol chieftain Noyai in Kipchak Khanate. | |
| 1290 | 1290/1300 Raids led by Alan prince Parejan to Georgia. | |
| 1298 | 1298/99 Alan merchants in Caffa (Crimea) during the sacking of the city by Mongol chieftain Noyai. | |
| 1300 | 1300/1 Civil war in Kipchak Khanate. Levy of the army by Jöge, son of Nogai, in ”country of Alans”, probably in Moldavia. | |
| 1300 | 1300/10 Raids led by Alan Bagatar in Georgia. | |
| 1301 | 1301/65 Trading of Alan slaves from Italian colonies in North of Black Sea to Europe. | |
| 1302 | 1302/4 Arrival of Alanian mercenaries contingent in Byzantium. Military activity against Turks. | |
| 1304 | Byzantines recruit Caucasus Alans as proxy allies. | |
| 1304 | 1304/6 Clashes between Alanian mercenaries and Catalan Grand Company in lands of Byzantine Empire. | |
| 1310 | 1310/23 Thirty thousand Alans in service of Mongol Yuan Emperors in China. | |
| 1314 | 1314/46 Defeat and expulsion of Alans from Georgia by king Georgi V Illustrious. | |
| 1318 | First recorded testimony of the presence of Alans (Yasses/Jasses) in Hungary. | |
| 1322 | Itiles (i.e. Itil) and Temeres (i.e Timur) Alans in service of Bulgarian Tsar George II Terter, in charge of the defence of Philippopolis against Byzantines. | |
| 1329 | Death of Sayf al-Din Bahadur As (i.e. Asian Bogatyr), renowned Alan Mamluk in Egypt. | |
| 1333 | Ibn Battuta’s stay in Kipchak Khanate. Muslim Alans in Sarai al Djadid, the capital city of Özbeg Kagan. | |
| 1336 | 1336-53 Embassy sent by Mongol Emperor Togon Temur and five Alan princes in China to Pope Benedict XII. Mission of Friar John of Marignolli in Khan Baliq (Beyjing). | |
| 1349 | John Cantacuzenus, ”Emperor of Alans”. | |
| 1395 | Tamerlan army invasion in Northern Caucasus, a mass murder of Alanian population. | |
| 1400 | 1400/34 Activity of Alan chieftain Arugtai in Mongolia. | |
| 1690 | 2nd half 17 – beg. 18-century Kabardins (Adyg group) populate plains of Alania. | |
| 1890 | Alans, like Scythians and Sarmatians, are suggested to be re-classified as Ossetian/Iranian/Indo-European speakers, and gradually become titled always only as “Iranian-speaking Alanians”, while the simple ”Alans” totally disappear. |
| Notes |
| 1. The name ”Alan” does not necessarily mean Caspian Alans/Masguts/Massagetes, because it may serve as locative adjective, which is seen in ethnically unrelated transparent ethnicon Yalan Kathai ( Steppe Kathai), as opposed to ”Ulu Kathai” (Great Kathai) and ”Bala Kathai” (Small Kathai) among Bashkir Kathai tribe, and similar type names ”Tungaur Yalan”, Yalan Yylayyr, Kuvakan Yalan, Yalan Isley, etc. Alan is one of Turkmen ethnic units, that is definitely a part of Caspian Alans/Masguts/Massagetes. |

Alans are still living. They live in the Caucasus, at the foot of Minga Tau (Elbrus)
Nowadays Karachaevichs And Balkars
—-
Аланы живы. Живут на Кавказе, у подножия Минги Тау (Эльбруса)
Ныне Карачаевчы И Балкарцы
Бар эль